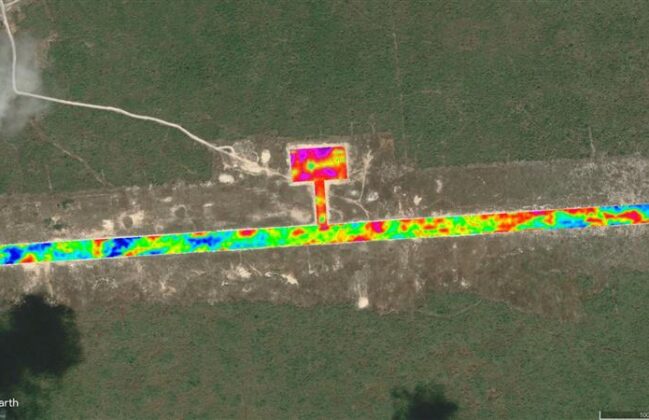
Barbuda 2D MASW
A planned 7,100-foot-long runway and associated taxiway, apron, and terminal/building area were assessed regarding possible karst for the design of a new airport in Barbuda. Compacted crushed rock pavement base course had been added to the runway, taxiway, and apron areas so we chose to utilize the two-dimensional (2D) Multi-Channel Analysis of Surface Waves (MASW) method for its ability to be efficiently performed on hard surfaces and to characterize subsurface variability associated with material stiffness/density.
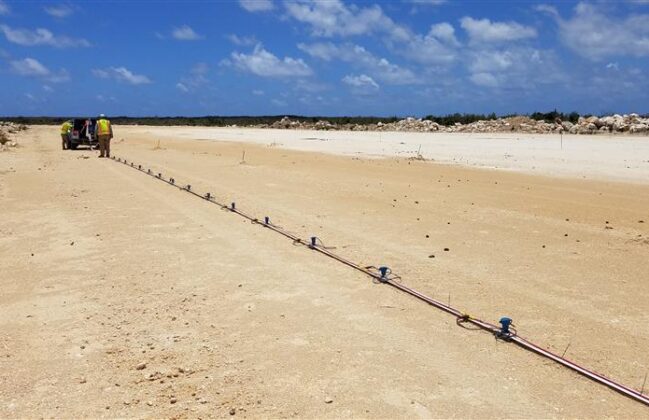
Nineteen 2D MASW profiles were collected at the site, totaling approximately 55,000 feet of data. A landstreamer with 4.5 Hz vertical geophones and accelerated weight drop (AWG) was used for the survey. Our final 2D profiles highlighted significant variability in shear wave velocity at the site, while our developed pseudo-3D models for each area provided additional lateral perspectives of the seismic data sets. Low shear-wave velocity areas were later correlated to porous limestone and cavities through our boring program.