Geosynthetic Design Considerations and QA/QC in the Waste Management Industry
November 14, 2023
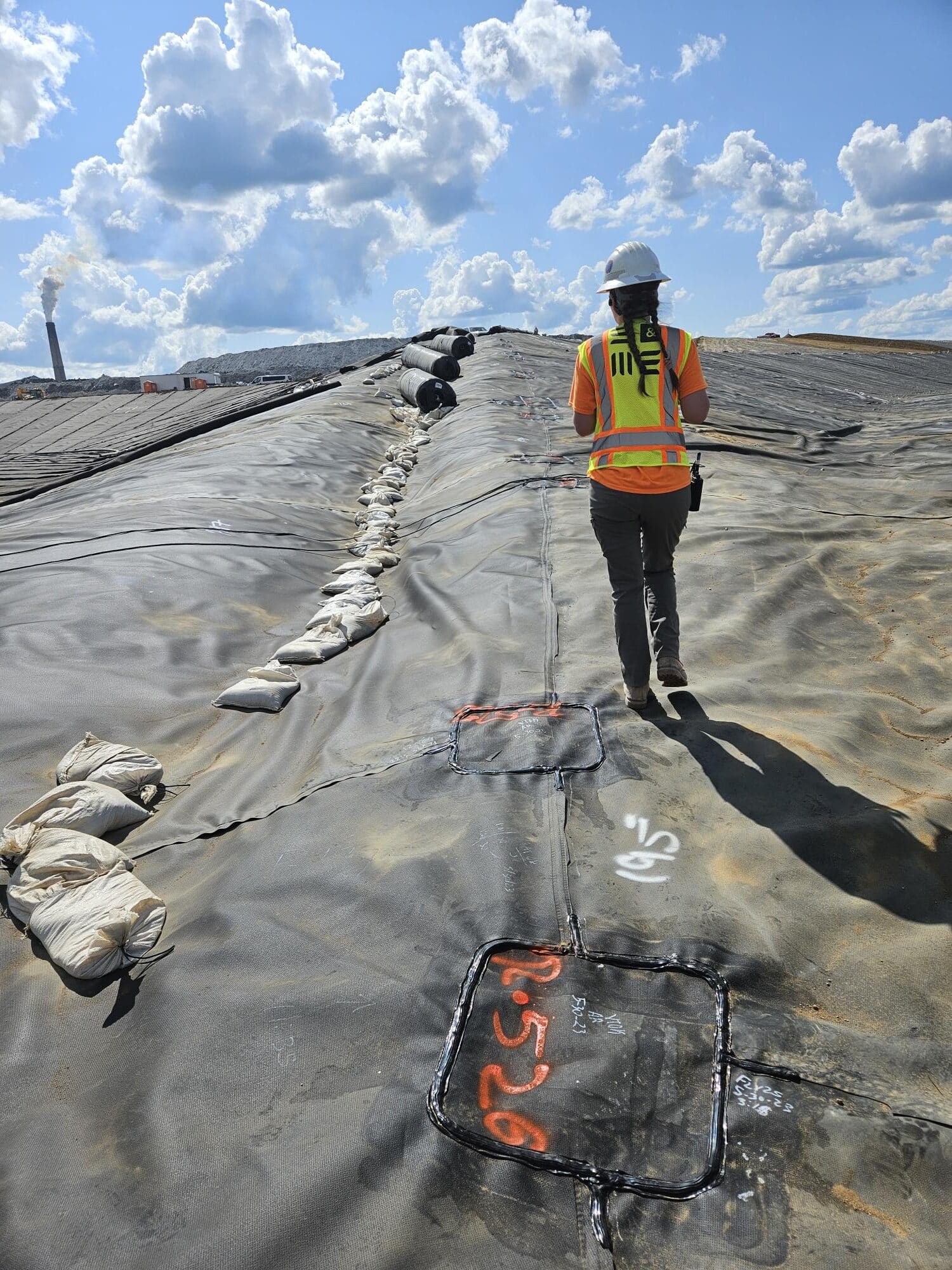
 Geosynthetics are manufactured products that are used in a wide range of engineering applications. They play a crucial role in the waste management industry, offering versatile solutions for containment, drainage, and protection and an effective means of isolating waste materials from soil and water, ensuring the environmental integrity of landfills.
Geosynthetics are manufactured products that are used in a wide range of engineering applications. They play a crucial role in the waste management industry, offering versatile solutions for containment, drainage, and protection and an effective means of isolating waste materials from soil and water, ensuring the environmental integrity of landfills.
Benefits of Geosynthetics
- Cost Effective: Geosynthetics can provide a cost-effective substitute for natural projects such as clay for a liner system and aggregate or sand for a drainage system.
- Uniform: Unlike natural products, geosynthetics are manufactured in a controlled environment to meet specified engineering parameters and then tested to ensure the engineering parameters are achieved. This provides a greater degree of uniformity and higher confidence in performance compared to natural materials.
- Efficiencies in Disposal: Relatively thin geosynthetics can be used in lieu of thicker layers of natural material, providing more airspace in the landfill for the disposal of waste material.
Geosynthetics Design Considerations
- Containment: Selecting an impervious geomembrane material that is compatible with the waste it contains is crucial to maintaining a reliable barrier between waste and the environment.
- Interface Stability: Landfill liner and cover systems often involve layering geosynthetics with other geosynthetics and natural materials. Slope stability calculations and interface friction testing are vital to ensure the structural integrity of these interfaces.
- Anchor Trench: Geosynthetics are secured using anchor trenches around the landfill perimeter. These trenches allow for movement in case of tension, preventing tears along the landfill’s sideslope.
- Drainage Capacity: Leachate is formed when rainwater filters through wastes placed in a landfill. When this liquid meets buried wastes, it leaches, or draws out, chemicals or constituents from those wastes. Adequate drainage capacity at the landfill’s base is essential to manage leachate effectively, reducing the pressure on the liner and the risk of leachate leakage.
Construction QA/QC Considerations
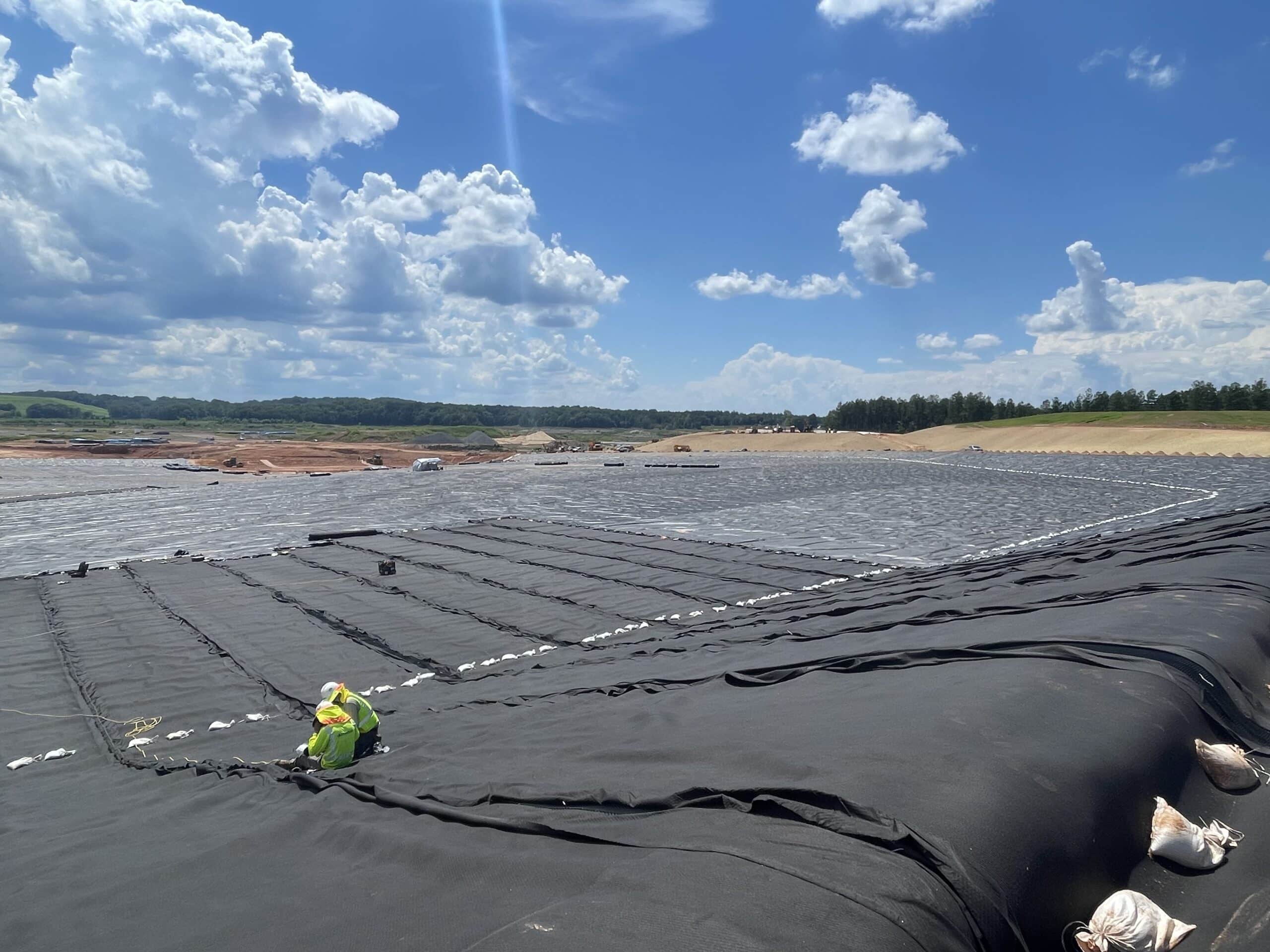
 Construction Quality Assurance (CQA) is a system that provides the owner and permitting agency assurance that the project was constructed as specified in the design. Construction quality assurance includes inspectors, verifications, audits, and evaluations of materials and workmanship necessary to determine and document the quality of the constructed project.
Construction Quality Assurance (CQA) is a system that provides the owner and permitting agency assurance that the project was constructed as specified in the design. Construction quality assurance includes inspectors, verifications, audits, and evaluations of materials and workmanship necessary to determine and document the quality of the constructed project.

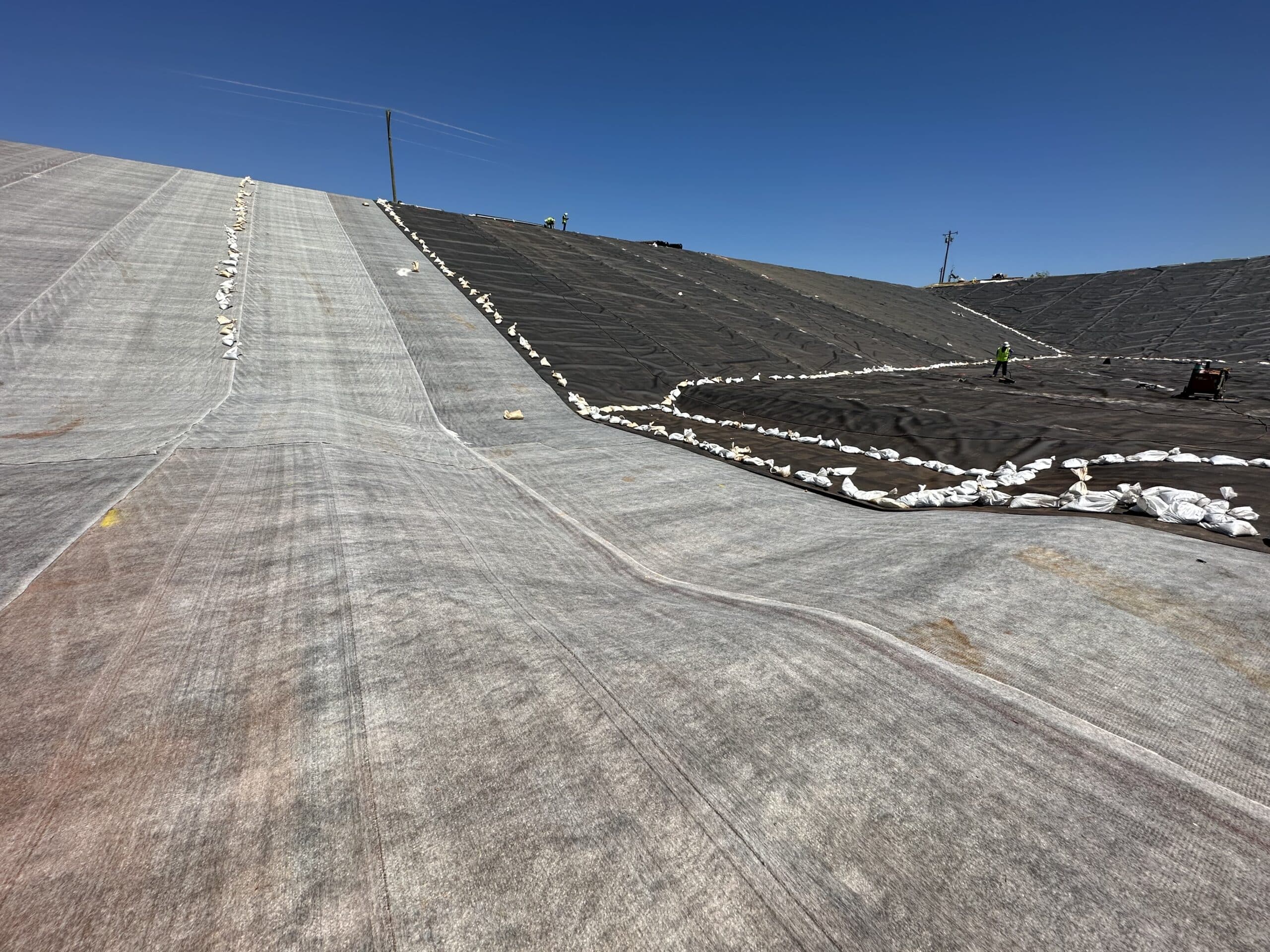
Construction Quality Control (CQC) refers to measures taken by the installer or contractor to determine compliance with the requirements for materials and workmanship as stated in the plans and specifications for the project. CQC is normally performed by the geosynthetics installer, or by the earthwork contractor, and is necessary to achieve quality in construction.
Construction QA/QC for Geosynthetic Installations focuses on the installation of geomembranes, geotextiles, geocomposites, geogrids, and/or geosynthetic clay liners. Special emphasis is given to establishing standard operating procedures for field inspections, documentation of tests and visual observations, and implementation of CQA plans.
CQA/CQA is applicable to all phases of geosynthetics manufacturing and installation:
- Manufacturing – Geosynthetic materials are tested as part of the manufacturing process to ensure that the materials meet project requirements. Sometimes two rounds of tests are performed: one set of tests by the manufacturer and a second round by a third-party laboratory. The Engineer should review and approve the Manufacturer and third-party test results prior to the material being shipped to the site.
- Delivery and storage – Once the materials are shipped to the site, they are inspected for quality and to ensure that the roll numbers that were delivered match the roll numbers that were tested and storage of the materials are within project requirements and standards.
- Construction – Observations and testing are performed to ensure that the materials are installed and seamed together in accordance with project requirements. Any defects that are observed are patched and repaired. We recommend conducting third-party Construction Quality Assurance in addition to the Installer’s CQC program to further ensure compliance with project requirements.
- Post-Construction – An Electric Leak Location (ELL) survey can be conducted after construction to evaluate the integrity of a geomembrane and ensure that construction activities did not damage the barrier component of the liner system.
Project Highlights
John R. Doutt Upground Reservoir – Columbus, Ohio
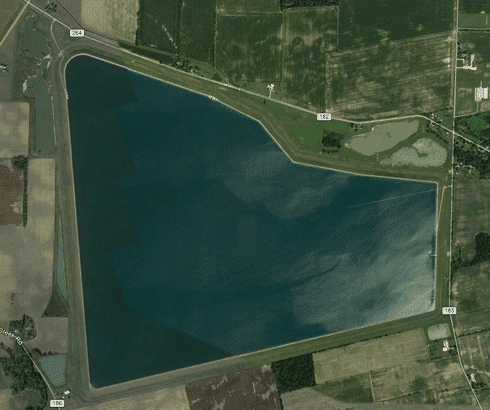 The John R. Doutt Upground Reservoir is the largest geosynthetic-lined structure in the United States. S&ME worked as part of the team for the design and construction of the 9.2 billion gallon reservoir. This is an on off-channel water supply reservoir for the City of Columbus. Owing to the presence of karst, the reservoir was lined with a 4-mil flexible polypropylene (fPP) geomembrane to reduce the potential for failure.
The John R. Doutt Upground Reservoir is the largest geosynthetic-lined structure in the United States. S&ME worked as part of the team for the design and construction of the 9.2 billion gallon reservoir. This is an on off-channel water supply reservoir for the City of Columbus. Owing to the presence of karst, the reservoir was lined with a 4-mil flexible polypropylene (fPP) geomembrane to reduce the potential for failure.
CCR Landfill Closure – Meridian, Mississippi
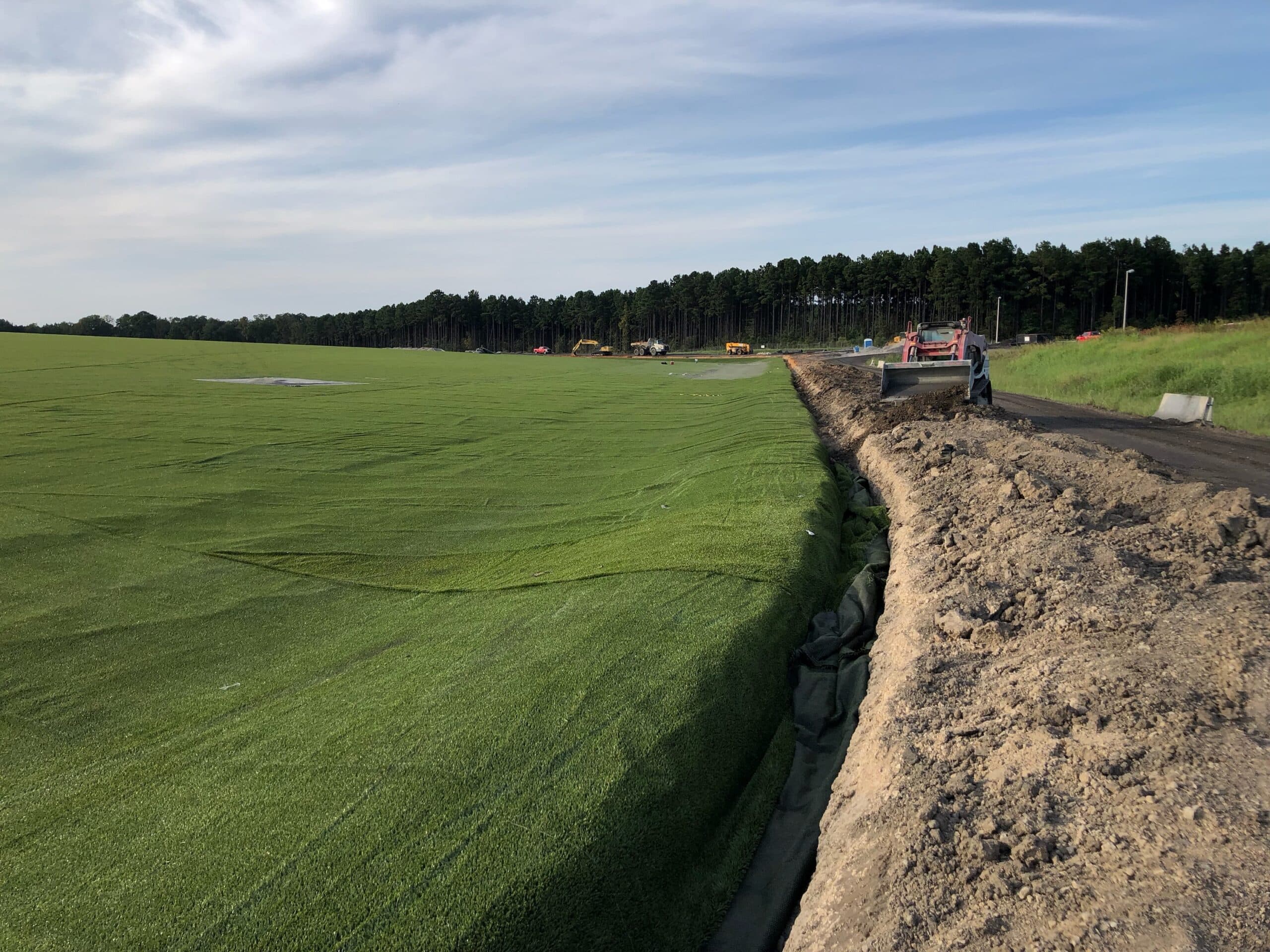 S&ME provided 4th party CQA services for a closure turf project. As part of this work, our teams observed, documented, and compiled the results of the Construction Quality Control (CQC) effort. Our teams were responsible for making recommendations for changes to project quality requirements as construction progressed.
S&ME provided 4th party CQA services for a closure turf project. As part of this work, our teams observed, documented, and compiled the results of the Construction Quality Control (CQC) effort. Our teams were responsible for making recommendations for changes to project quality requirements as construction progressed.
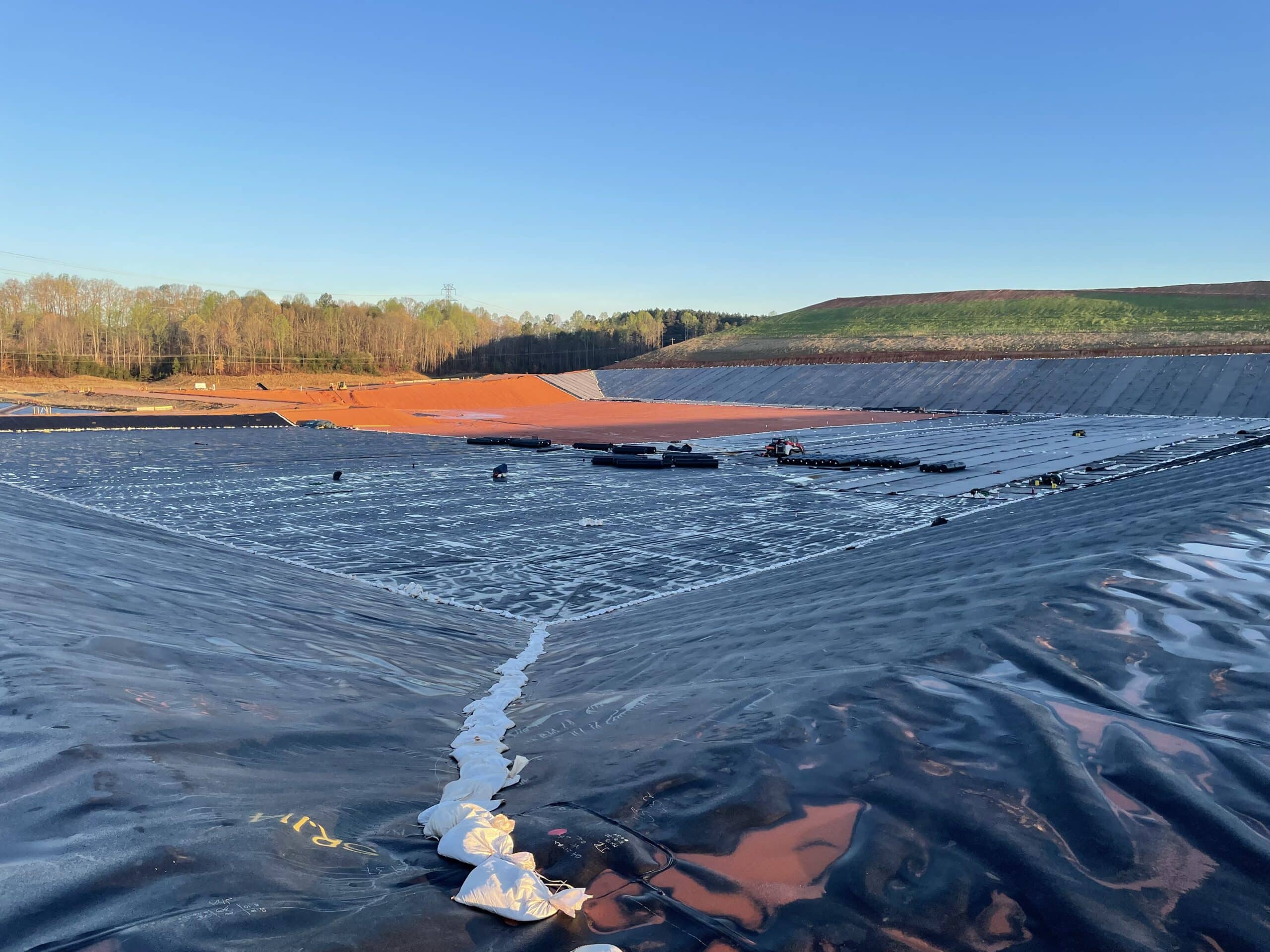
CCR Landfill Construction Projects- North and South Carolina
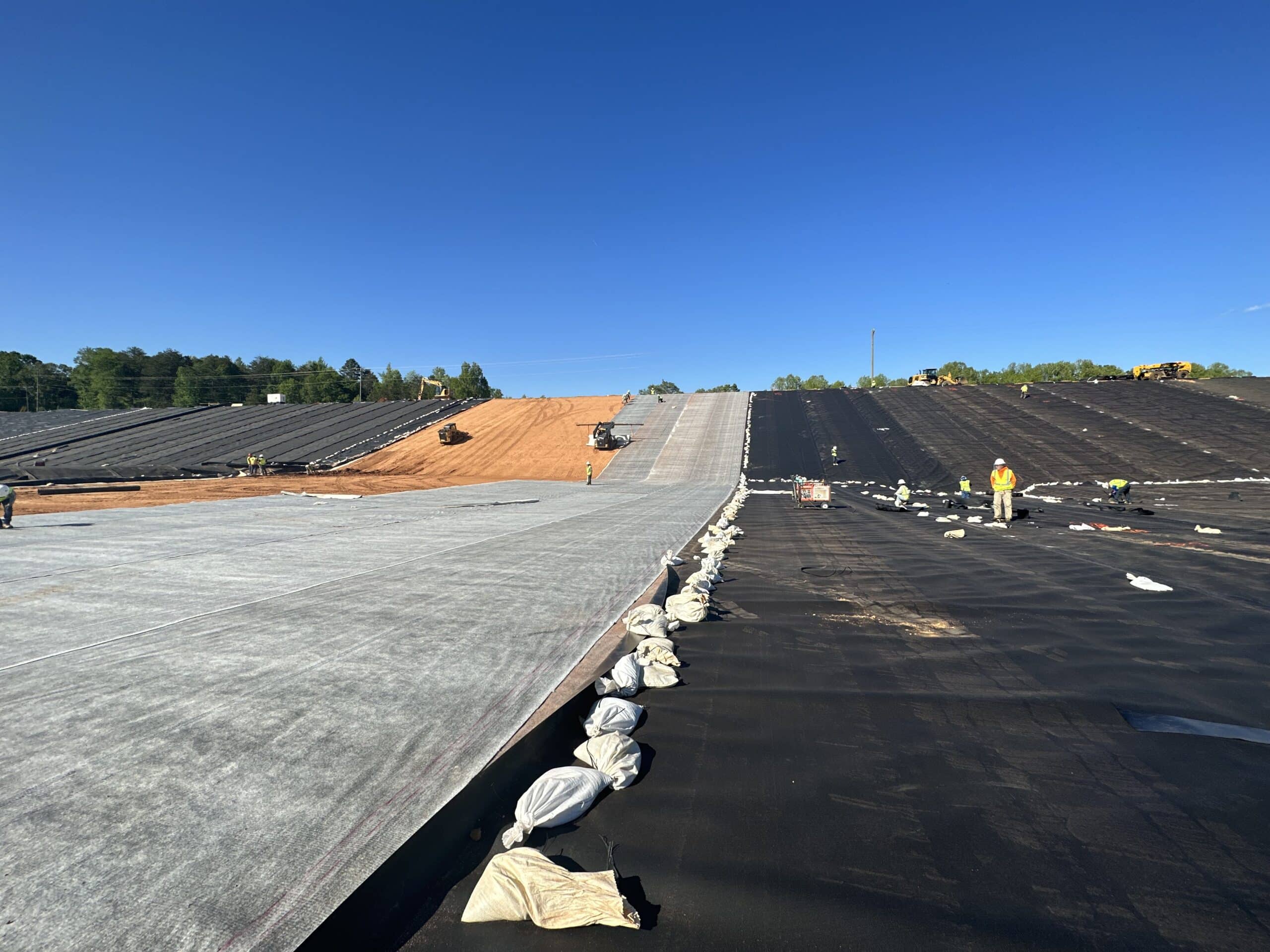 S&ME is serving as the Primary CQA Consultant on various CCR landfill construction projects and closures that will hold over 40 million cubic yards of CCR material throughout the Carolinas. The primary role of S&ME is to certify that the projects have been constructed in general accordance with the permitting requirements, contract documents, specifications, and regulatory requirements. Our team provides CQA oversight of multi-layer geosynthetics liner systems, geosynthetic clay liner systems, and engineered closure systems from construction to operations to closure of the various landfills.
S&ME is serving as the Primary CQA Consultant on various CCR landfill construction projects and closures that will hold over 40 million cubic yards of CCR material throughout the Carolinas. The primary role of S&ME is to certify that the projects have been constructed in general accordance with the permitting requirements, contract documents, specifications, and regulatory requirements. Our team provides CQA oversight of multi-layer geosynthetics liner systems, geosynthetic clay liner systems, and engineered closure systems from construction to operations to closure of the various landfills.

